Raster Rubber Sheeting

The preview tool allows you to see the extents of the transformed image before you actually apply the changes.
Raster rubber sheeting. As a weather resistant rubber this epdm sheet rubber is commonly used in industrial applications and machinery that are exposed to the elements. This is sometimes referred to as image to vector conflation. Damage from rainstorms pollution and the sun will occur at a slower rate compared to a fully exposed epdm rubber when compared to other elastomers like sbr nitrile or neoprene.
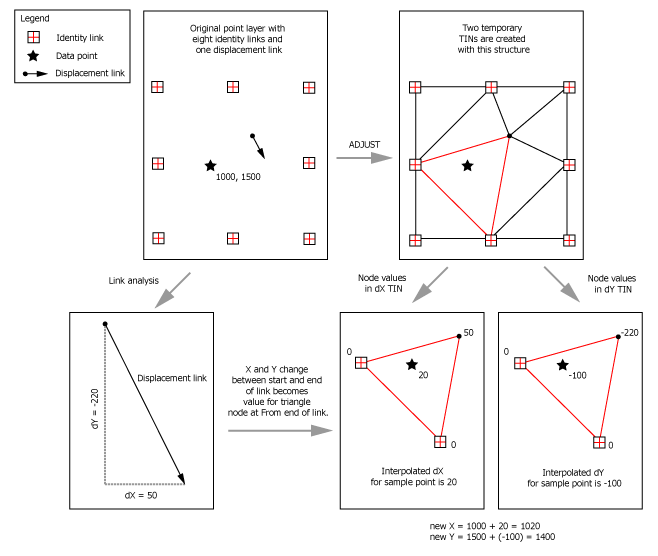
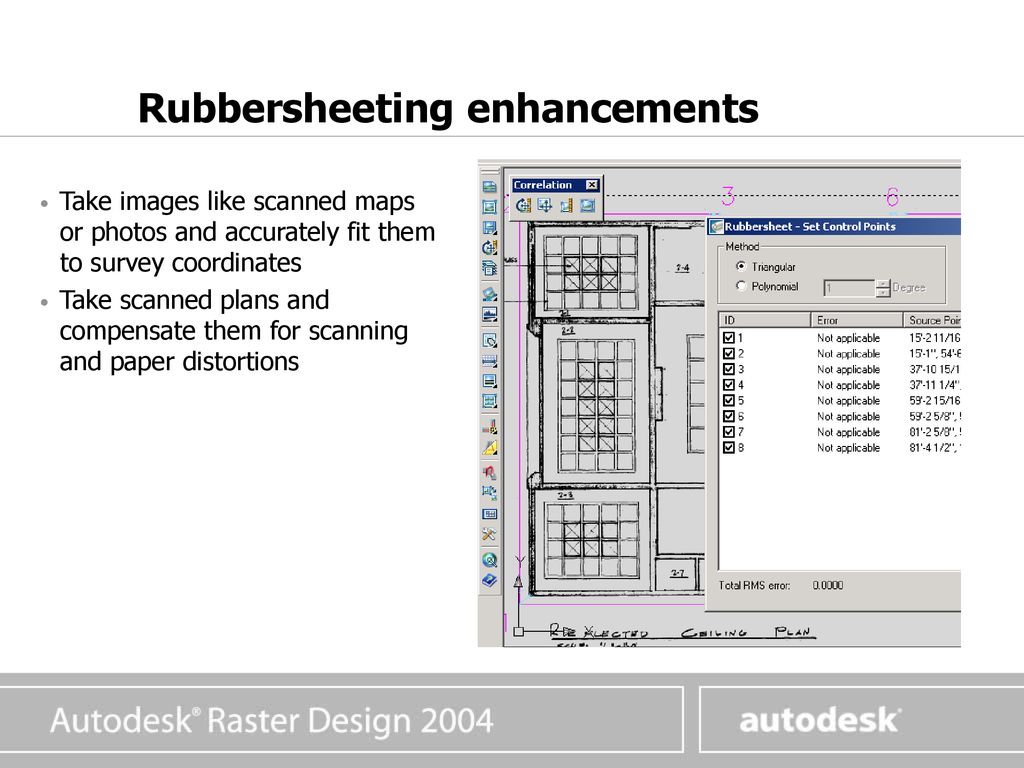
Linear this method creates a quick tin surface but does not really take into account the neighborhood. Select the image to rubbersheet. Conflation applications use rubbersheeting to align layers in preparation for transferring attributes.
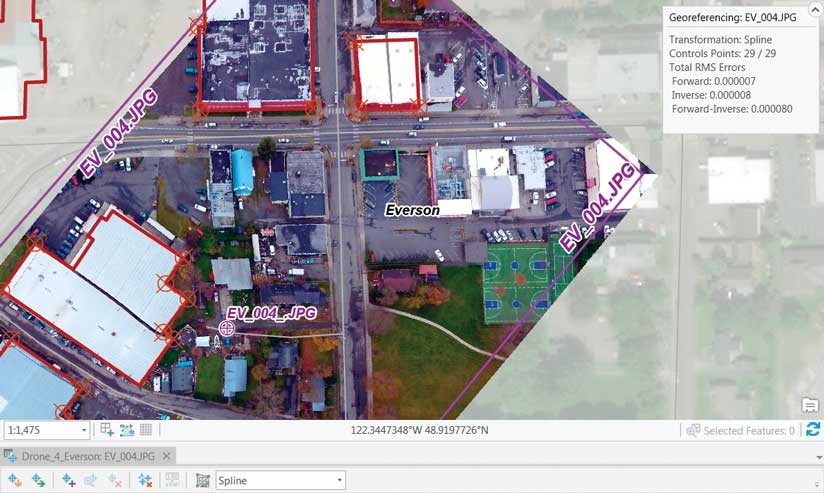
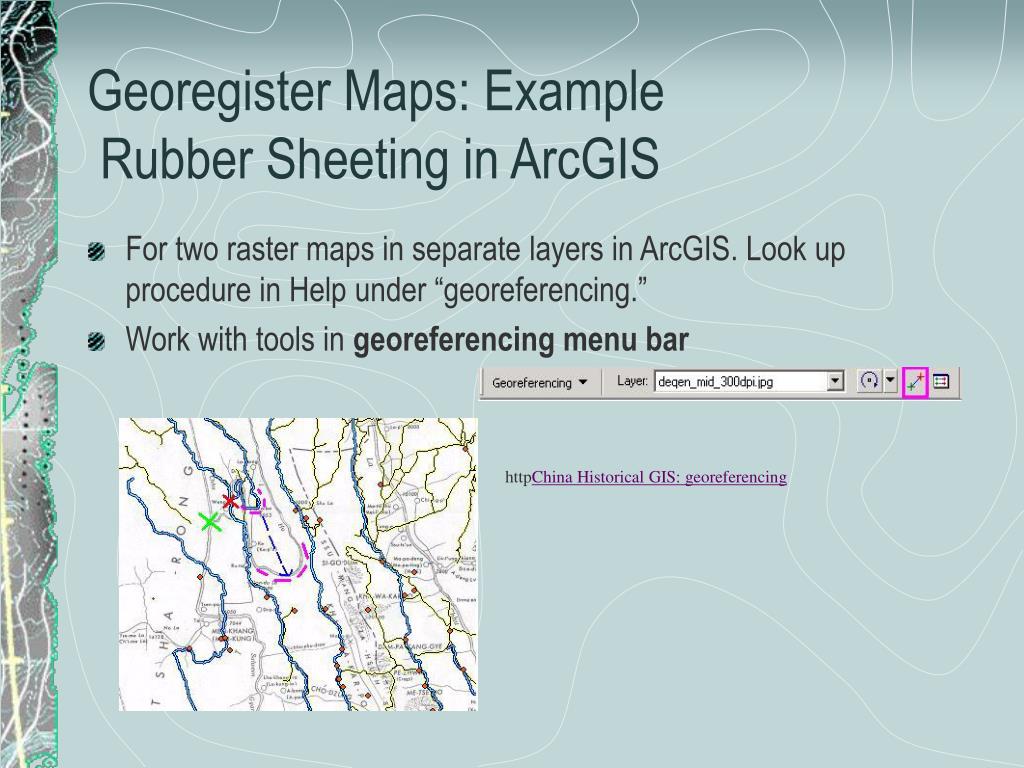
Rubbersheeting is commonly used after a transformation to further refine the accuracy of the features to an existing layer or raster dataset. See about spatial adjustment rubbersheeting for more details. In cartography rubber sheeting refers to the process by which a layer is distorted to allow it to be seamlessly joined to an adjacent geographic layer of matching imagery such as satellite imagery most commonly vector cartographic data which are digital maps. The method parameter determines the interpolation method used to create the temporary tins in rubbersheeting.
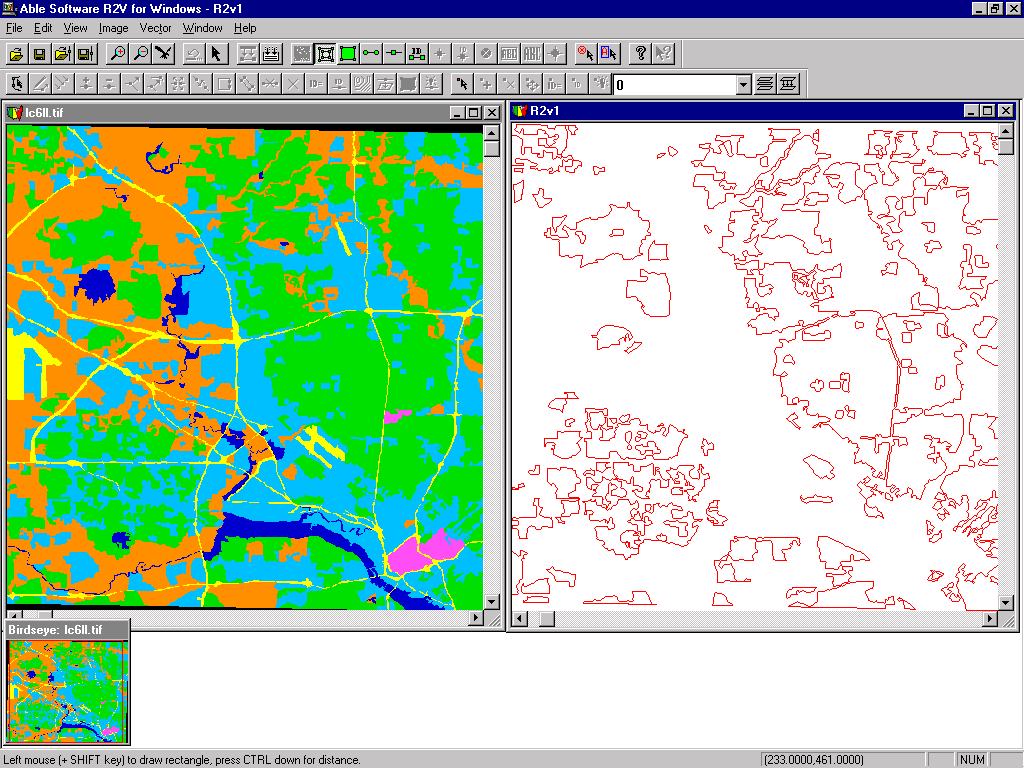
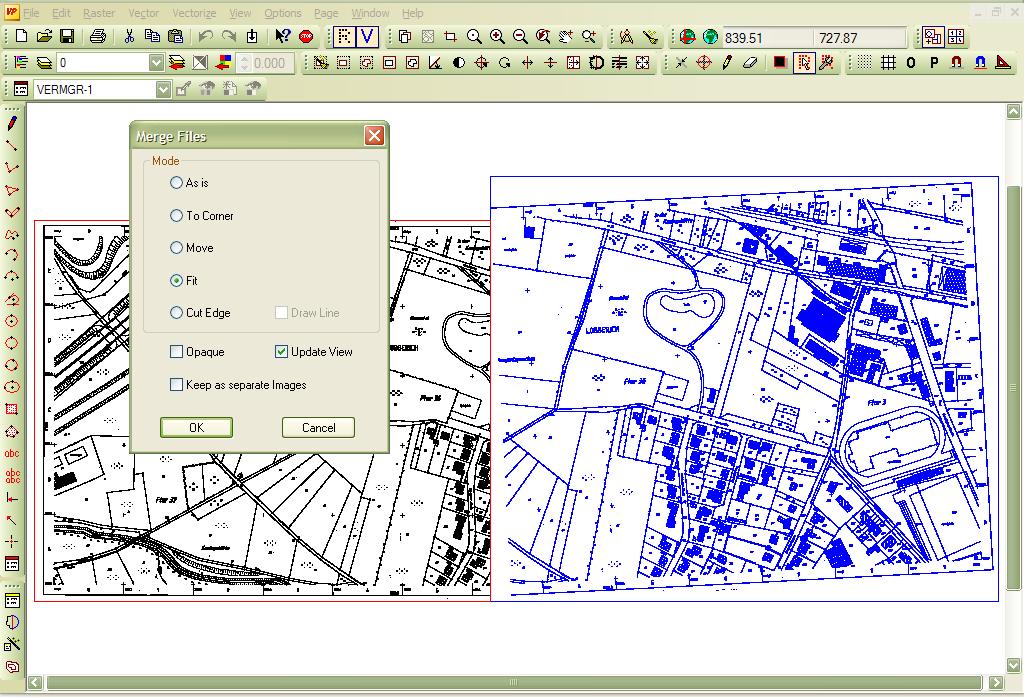
The autocad raster design toolset helps you convert raster images into dwg objects with its powerful vectorization tools. It is slightly faster and produces good results when you have many rubbersheet links spread uniformly over the data. Click raster menu correlaterubbersheet. Autocad raster design toolset does not limit the number of control points you can use.
If there is only one image in the current drawing that image is automatically selected.